Diabetes is a long-term health condition that affects how your body uses blood sugar (glucose). Proper diabetes management is essential to prevent complications and live a healthy, active life. Whether you have Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, or prediabetes, making smart lifestyle choices can help you control your blood sugar levels effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss practical and easy diabetes management tips for a healthy lifestyle that you can start following today.
1. Follow a Balanced and Diabetes-Friendly Diet

Healthy eating is the foundation of diabetes management. A balanced diet helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevents sudden spikes.
Key Dietary Tips:
- Choose low glycemic index (GI) foods.
- Eat more fiber-rich foods like vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Include lean protein such as beans, lentils, eggs, fish, and tofu.
- Limit refined sugar, white bread, and processed snacks.
- Avoid sugary drinks and packaged juices.
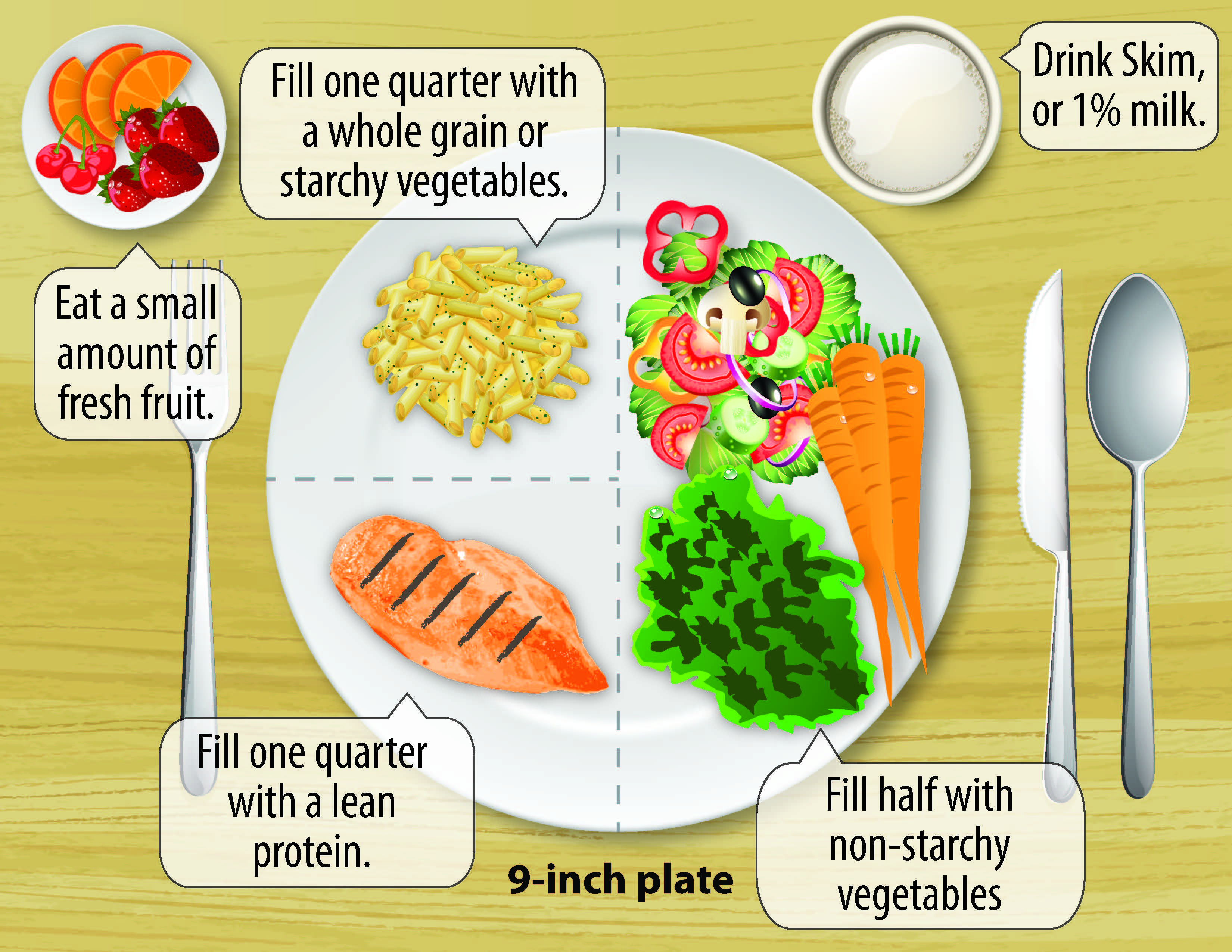
Portion Control Matters
Even healthy foods can raise blood sugar if eaten in large amounts. Use the plate method:
- Half plate: Non-starchy vegetables
- One-quarter: Lean protein
- One-quarter: Whole grains
Eating smaller, frequent meals helps prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
2. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps lower blood sugar levels naturally.
Best Exercises for Diabetes:
- Brisk walking (30 minutes daily)
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Yoga
- Light strength training
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week. Even small changes like taking stairs or walking after meals can make a big difference.
3. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Monitoring your blood glucose levels helps you understand how food, exercise, and stress affect your body.
- Use a glucometer as advised by your doctor.
- Maintain a blood sugar diary.
- Check fasting and post-meal levels.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s target range.
Regular monitoring prevents complications and allows timely adjustments in diet or medication.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight increases insulin resistance, especially in Type 2 diabetes. Losing even 5–10% of body weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
Weight Management Tips:
- Avoid crash dieting.
- Combine diet and exercise.
- Stay consistent.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid late-night eating.
Healthy weight loss should be gradual and sustainable.
5. Manage Stress Effectively



Stress can raise blood sugar levels by releasing stress hormones like cortisol.
Stress Management Techniques:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Listening to calming music
- Spending time in nature
- Practicing gratitude
Even 10–15 minutes of daily relaxation can help stabilize your blood sugar levels.
6. Get Quality Sleep
Poor sleep affects insulin sensitivity and can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Sleep Tips:
- Sleep 7–8 hours daily.
- Avoid screens before bedtime.
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Limit caffeine in the evening.
Good sleep supports hormone balance and overall diabetes management.
7. Take Medications as Prescribed
If your doctor has prescribed insulin or oral medication, take them exactly as directed.
- Do not skip doses.
- Do not self-adjust medication.
- Consult your doctor if you notice unusual symptoms.
Medication combined with lifestyle changes gives the best results.
8. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water helps flush out excess sugar through urine and prevents dehydration.
- Drink 8–10 glasses of water daily.
- Avoid sugary beverages.
- Choose herbal teas or infused water.
Hydration plays a vital role in maintaining stable blood sugar.
9. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Smoking increases the risk of heart disease and diabetes complications. Alcohol can cause sudden blood sugar fluctuations.
- Quit smoking immediately.
- If consuming alcohol, do so in moderation and with food.
- Always check blood sugar levels after drinking.
10. Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine check-ups help detect complications early.
Important Tests:
- HbA1c test (every 3–6 months)
- Eye examination
- Kidney function tests
- Foot examination
- Cholesterol and blood pressure monitoring
Prevention is better than cure when managing diabetes.
Long-Term Complications of Poor Diabetes Management
If diabetes is not managed properly, it can lead to:
- Heart disease
- Kidney damage
- Vision problems
- Nerve damage
- Foot ulcers
Proper lifestyle management significantly reduces these risks.
Final Thoughts
Living with diabetes does not mean you cannot live a healthy and fulfilling life. By following proper diabetes management tips, including healthy eating, regular exercise, stress control, proper sleep, and routine monitoring, you can maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Consistency is the key. Small daily improvements lead to long-term health benefits. Always consult your healthcare provider before making major lifestyle changes.
Start today, stay disciplined, and take control of your health naturally.










Leave a comment